Let’s be honest here. You’ve probably spent countless hours creating amazing content for your website, but it’s just sitting there on page 3 or 4 of Google, collecting digital dust. And you’re wondering why your competitors are ranking higher when your content is clearly better.
Here’s the thing: great content alone won’t cut it anymore. You need on-page SEO working in your favour, and you need it done right.
I’ve been in the digital marketing trenches for years, and I’ve seen businesses transform their search rankings just by mastering on-page SEO techniques. We’re talking about jumping from page 5 to page 1 in a matter of weeks. So yes, this stuff actually works when you apply it correctly.
In this guide, I’m going to walk you through 11 battle-tested on-page SEO tactics that have helped countless websites (including those managed by Digi Segment and HV Digital Marketing) climb to the top of search results. You’ll learn exactly what to do, how to do it, and why it matters. No fluff, no outdated advice—just proven strategies that deliver real results in 2025.
What Is On-Page SEO? (And Why It Matters in 2025)
Before we dive into the tactics, let’s get crystal clear on what on-page SEO actually means. Because if you’re going to invest time in this, you need to understand why it’s so powerful.
On-page SEO is all about optimizing individual web pages to rank higher and earn more relevant traffic from search engines. Think of it as making your website pages irresistible to both Google and your human visitors. It’s everything you can control directly on your website—your content, your HTML tags, your images, your internal links, and even how fast your pages load.
The Core Elements of On-Page SEO
On-page SEO optimization isn’t just one thing. It’s a collection of elements working together like a well-oiled machine. You’ve got your title tags telling Google what your page is about, your meta descriptions convincing people to click, your header tags organizing your content, and your URLs giving everyone a clear roadmap.
But it goes deeper than that. Your keyword placement matters because it signals relevance. Your internal linking structure matters because it helps Google understand your site architecture and distributes authority. Your image optimization matters because page speed impacts rankings. And your content quality matters because Google’s algorithms are smarter than ever at detecting valuable, helpful content.
How On-Page SEO Impacts Your Rankings
Here’s what most people don’t realize: on-page SEO is your direct line of communication with Google’s ranking algorithm. When you optimize your pages correctly, you’re essentially speaking Google’s language and telling it exactly what your content is about, who it’s for, and why it deserves to rank.
Google uses hundreds of ranking factors, but many of the most important ones fall under on-page SEO best practices. Your title tags, your content depth, your user experience signals—these all contribute to where you land in search results. And unlike off-page factors like backlinks (which you can’t fully control), on-page SEO factors are entirely in your hands.
Tactic #1: Master Keyword Research & Strategic Placement
Look, I’m going to start with the foundation because everything else builds on this. If you mess up your keyword research, nothing else matters. You’ll be optimizing for terms nobody searches for or terms you’ll never rank for.
How to Find High-Impact Keywords
Finding the right keywords isn’t about guessing what people might search for. It’s about data-driven research that reveals actual search demand and realistic ranking opportunities.
Start with your main topic—in this case, on-page SEO for websites. Then use tools like Google Keyword Planner, SEMrush, or Ahrefs to uncover related terms. But here’s the smart approach: don’t just chase high-volume keywords. Look for that sweet spot where search volume meets low competition.
For instance, “on-page SEO strategy” might have decent volume and be more achievable than the ultra-competitive “SEO.” Long-tail variations like “on-page SEO checklist for beginners” often convert better anyway because they show specific search intent.
The 4 Critical Places to Position Your Keywords
Once you’ve got your keywords, placement becomes everything. Random keyword sprinkling doesn’t work and actually hurts your rankings. You need strategic, natural placement in specific locations that matter most to search engines.
Title Tags & Meta Descriptions
Your title tag is prime real estate. It’s the first thing Google reads and the first thing users see in search results. Place your primary keyword near the beginning of your title tag, but make sure it still reads naturally and compels clicks.
Your meta description doesn’t directly impact rankings, but it absolutely affects click-through rates. Include your target keyword here too, along with a compelling reason to click. Think of it as your elevator pitch in 155 characters or less.
Headers (H1, H2, H3)
Your H1 should include your main keyword—this is non-negotiable. But don’t stop there. Sprinkle related keywords and variations throughout your H2 and H3 tags. This creates a clear content hierarchy and helps Google understand your topic depth.
For example, if your main keyword is “on-page SEO techniques,” your subheadings might naturally include variations like “on-page SEO optimization tips” or “on-page SEO best practices for rankings.”
First 100 Words of Content
Google pays special attention to your opening paragraph because it sets the context for everything that follows. Work your primary keyword into the first 100 words naturally. Don’t force it—if it feels awkward, rewrite until it flows smoothly.
Image Alt Text & URLs
People often overlook these, but they’re goldmines for on-page SEO optimization. Your URL should be short, descriptive, and include your keyword. So instead of “website.com/post-12345,” aim for “website.com/on-page-seo-guide.”
Image alt text serves dual purposes: accessibility and SEO. Describe what’s in the image while naturally incorporating relevant keywords when appropriate.
Tactic #2: Craft Irresistible Title Tags That Boost CTR
Your title tag is your first impression in search results, and you know what they say about first impressions. A weak title tag means people scroll right past you, even if you’re ranking on page one.
The Perfect Title Tag Formula
After testing hundreds of title tags, I’ve found a formula that consistently delivers high click-through rates. It goes like this: [Number] + [Adjective] + [Keyword] + [Promise/Benefit].
For example: “11 Proven On-Page SEO Tactics That Skyrocket Rankings” hits all the marks. The number creates curiosity, “proven” adds credibility, the keyword is front and center, and “skyrocket rankings” promises a clear benefit.
Keep your titles between 50-60 characters so they don’t get cut off in search results. And always make sure they accurately represent your content—clickbait might get clicks initially, but it destroys your rankings long-term because of high bounce rates.
Common Title Tag Mistakes to Avoid
I see these mistakes everywhere, and they’re killing people’s rankings. First, stuffing multiple keywords into your title tag. It looks spammy and Google actually penalizes this now.
Second, creating generic titles like “Home” or “Services.” These tell Google nothing about your content and give users no reason to click. Be specific and descriptive.
Third, duplicating title tags across multiple pages. Every page on your site needs a unique title tag that accurately describes that specific page’s content.
Tactic #3: Optimize Meta Descriptions for Maximum Clicks
Meta descriptions don’t directly impact rankings, but they’re incredibly powerful for boosting click-through rates. And higher CTR signals to Google that your content is valuable, which indirectly boosts your rankings.
What Makes a Meta Description Compelling
Think of your meta description as ad copy. You’ve got 155 characters to convince someone that your page has exactly what they’re looking for. That’s not a lot of space, so every word counts.
Start with your keyword to show relevance. Then immediately follow with a clear benefit or solution. Address the searcher’s pain point and promise a resolution. Add urgency or curiosity when appropriate.
For example: “Discover 11 on-page SEO techniques that top-ranking sites use to dominate Google. Step-by-step guide with real examples and quick wins you can implement today.”
Meta Description Best Practices
Always include a call-to-action, even if it’s subtle. Phrases like “Learn how,” “Discover,” or “Get started” encourage clicks. But avoid clickbait promises you can’t deliver on.
Keep your descriptions unique for every page. Duplicate meta descriptions are a wasted opportunity and confuse both users and search engines about what makes each page different.
And here’s a pro tip from the team at HV Digital Marketing: test different meta descriptions. You can update them anytime, and sometimes a small tweak can dramatically improve your CTR.
Tactic #4: Structure Content with Header Tags (H1-H6)
Meta descriptions don’t directly impact rankings, but they’re incredibly powerful for boosting click-through rates. And higher CTR signals to Google that your content is valuable, which indirectly boosts your rankings.
Why Header Hierarchy Matters for SEO
Google’s algorithms scan your header tags to understand your content’s organization and main topics. A proper header hierarchy tells Google, “Here’s my main topic, here are my subtopics, and here’s how they all relate.”
Your H1 is your main headline—use only one per page and make sure it includes your primary keyword. Then use H2s for your main sections, H3s for subsections under those H2s, and so on. Think of it like an outline from school: H1 is your title, H2s are your Roman numerals, H3s are your capital letters.
How to Use Headers to Improve Readability
Beyond SEO, headers make your content scannable. Most people don’t read every word—they scan for relevant sections. Clear, descriptive headers guide them to exactly what they need.
Use your headers to break up large blocks of text. Nobody wants to face a wall of 500 words. Every 200-300 words, add a subheading that previews what’s coming next. This keeps readers engaged and reduces bounce rates.
Make your headers descriptive and interesting. Instead of “Benefits,” try “How This Strategy Doubled Our Organic Traffic in 60 Days.” Specificity and intrigue keep people reading.
Tactic #5: Create SEO-Friendly URL Structures
URLs might seem like a minor detail, but they impact both your rankings and your click-through rates. A clean, descriptive URL builds trust and tells users exactly what to expect.
URL Optimization Best Practices
Keep your URLs short and sweet. Remove unnecessary words like “and,” “the,” or “of.” So instead of “website.com/the-complete-guide-to-on-page-seo-optimization-for-websites,” go with “website.com/on-page-seo-guide.”
Include your target keyword in the URL. This reinforces your page’s topic and provides another relevance signal to search engines. But don’t stuff multiple keywords—one primary keyword is enough.
Use hyphens to separate words, not underscores. Google reads hyphens as spaces but treats underscores as connectors. So “on-page-seo” is interpreted as three words, while “on_page_seo” looks like one long string.
What to Avoid in Your URLs
Never use special characters, session IDs, or random parameter strings in your URLs. They look suspicious to users and cause indexing issues for search engines. Keep it simple: lowercase letters, numbers, and hyphens only.
Avoid changing URLs once your content is published and indexed. URL changes break backlinks and lose accumulated SEO value. If you must change a URL, always set up a 301 redirect from the old URL to the new one.
Tactic #6: Optimize Images for Speed & Search Visibility
Images make your content engaging, but they can also slow down your site if not optimized properly. And page speed is a confirmed ranking factor, especially for mobile searches.
Image Compression Without Quality Loss
Large image files are the number one cause of slow page loads. But you don’t have to sacrifice quality to reduce file size. Tools like TinyPNG, ImageOptim, or built-in WordPress plugins can compress images by 50-70% without visible quality loss.
Before uploading images, compress them. A 2MB image can usually be reduced to 200-300KB without anyone noticing the difference. Those seconds saved add up and significantly improve user experience.
Writing Effective Alt Text
Alt text optimization serves two purposes: it helps visually impaired users understand your images, and it gives search engines context about your visual content.
Write descriptive alt text that explains what’s in the image. Include relevant keywords when it makes sense, but never stuff keywords unnaturally. For example, good alt text: “Person analyzing on-page SEO checklist on laptop screen.” Bad alt text: “on-page SEO on-page SEO techniques on-page SEO optimization.”
Choosing the Right Image Format (WebP vs. JPEG vs. PNG)
WebP is the new king of image formats. It provides better compression than JPEG and PNG while maintaining quality, and it’s supported by all modern browsers. Use WebP whenever possible.
For photos, JPEG works well if WebP isn’t an option. For graphics with transparency or text, PNG is your best bet. And forget about GIFs for static images—they’re inefficient and unnecessarily large.
Tactic #7: Implement Internal Linking Strategy
Internal linking is one of the most underutilized on-page SEO techniques, and it’s a shame because it’s incredibly powerful for boosting rankings and keeping visitors engaged.
How Internal Links Boost Page Authority
Every internal link passes authority (also called “link juice”) from one page to another. When you link from a high-authority page to a newer or weaker page, you’re essentially vouching for that content and helping it rank better.
Internal links also help Google discover and index your content faster. They create pathways for crawlers to navigate your entire site structure efficiently.
Best Practices for Anchor Text
Your anchor text—the clickable words in a link—should be descriptive and relevant. Instead of “click here” or “read more,” use keyword-rich phrases that tell users and search engines what they’ll find when they click.
For example, linking to an article about keyword research with anchor text like “keyword research strategies” or “how to find high-impact keywords” is much more valuable than generic anchors.
Vary your anchor text naturally. Don’t use the exact same phrase for every internal link to a page. Mix it up with variations and related terms.
The Strategic Hub & Spoke Model
The experts at Digi Segment recommend using a hub-and-spoke model for internal linking. Create comprehensive “pillar” content on broad topics, then link out to more specific “spoke” articles that dive deep into subtopics.
Those spoke articles should link back to the hub and to each other when relevant. This creates a tight content cluster that signals topical authority to Google and provides tremendous value to users exploring your content.
Tactic #8: Enhance User Experience with Core Web Vitals
Google’s Core Web Vitals are now official ranking factors, and they measure real user experience metrics. If your site provides a poor experience, your rankings will suffer no matter how good your content is.
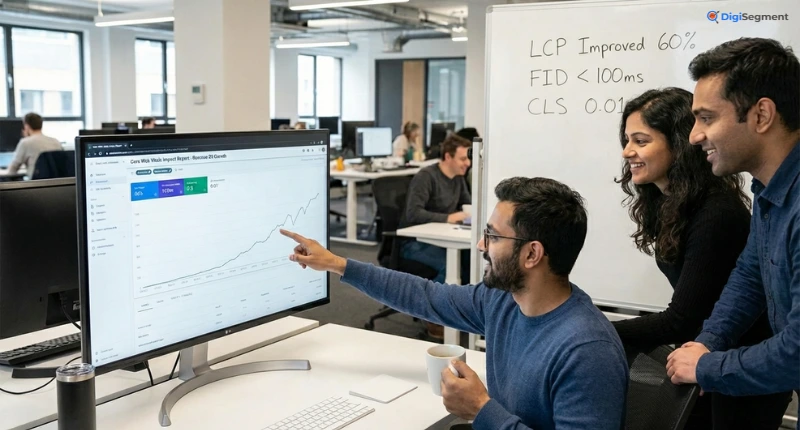
Understanding LCP, FID, and CLS
Core Web Vitals consist of three main metrics. Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) measures loading performance—how long it takes for the main content to appear. You want this under 2.5 seconds.
First Input Delay (FID) measures interactivity—how quickly your page responds to user interactions like clicks or taps. Aim for under 100 milliseconds.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) measures visual stability—how much your page layout shifts unexpectedly while loading. You want a score under 0.1.
Quick Fixes to Improve Core Web Vitals
Optimize Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
Improve your LCP by optimizing your largest image or text block. Compress images, use lazy loading for below-the-fold content, and minimize render-blocking resources like CSS and JavaScript files.
Consider using a CDN to serve static assets faster. Remove unnecessary third-party scripts that slow down initial page loads.
Reduce First Input Delay (FID)
Break up long JavaScript tasks into smaller, asynchronous chunks. Minimize third-party code that runs on page load. Use browser caching so returning visitors load your site faster.
Minimize Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Always specify width and height attributes for images and videos so browsers reserve the correct space before they load. Avoid inserting content above existing content unless it’s in response to a user interaction.
Use font-display: swap in your CSS to prevent invisible text during font loading. And never use ads or embeds without reserved space.
Tactic #9: Leverage Schema Markup for Rich Snippets
Schema markup is like giving Google a cheat sheet about your content. It helps search engines understand your content context and can earn you eye-catching rich snippets that increase click-through rates.
What Is Schema Markup?
Schema markup is structured data code you add to your HTML that explicitly tells search engines what your content represents. Is it an article? A product? A recipe? A local business? Schema markup clarifies this.
Rich snippets—those enhanced search results with star ratings, images, or additional info—come from schema markup. They make your listing stand out and can dramatically increase clicks.
Types of Schema That Drive Results
Article Schema
Article schema tells Google that your content is an article and provides details like publish date, author, and headline. This is essential for news and blog content to appear in Google News and earn article rich snippets.
FAQ Schema
FAQ schema displays your questions and answers directly in search results, often in an expandable format. This takes up more real estate on the results page and positions you as a helpful resource.
How-To Schema
How-to schema is perfect for instructional content. It can display your steps directly in search results, with images and even videos, making your listing incredibly valuable and clickable.
Product Schema
If you sell products, product schema is non-negotiable. It enables rich snippets with pricing, availability, and review ratings that significantly increase purchase intent clicks.
Tactic #10: Optimize Content Quality & Readability
All the technical on-page SEO optimization in the world won’t save poorly written content. Google’s algorithms are incredibly sophisticated at evaluating content quality, and user behavior metrics reveal the truth about whether your content delivers value.
Writing for Humans First, Search Engines Second
This sounds obvious, but so many people get it backward. They write for algorithms and end up with robotic, keyword-stuffed nonsense that nobody wants to read.
Start with your reader’s needs and questions. What problem are they trying to solve? What information would genuinely help them? Answer those questions thoroughly and conversationally, and the SEO will follow naturally.
Use real examples, tell stories, and inject personality. Generic, encyclopedic content doesn’t engage readers or earn rankings anymore. Google can detect when people quickly return to search results because your content didn’t satisfy them.
The E-E-A-T Framework (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trust)
Google’s quality guidelines emphasize E-E-A-T: Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. This matters more than ever in 2025.
Demonstrate experience by sharing first-hand knowledge and real examples. Show expertise through depth of coverage and accuracy. Build authoritativeness with proper citations and credentials. Establish trust through transparency, secure site connections, and clear contact information.
For topics that impact health, finances, or safety (“Your Money or Your Life” topics), E-E-A-T is absolutely critical. Google scrutinizes these pages intensely.
Improving Readability with Short Paragraphs & Bullet Points
Break up your content visually. Nobody enjoys reading dense paragraphs on a screen. Keep paragraphs to 2-4 sentences maximum.
Use bullet points and numbered lists to make information scannable. When you have multiple related items or steps, list format is almost always clearer than paragraph form.
Vary your sentence length. Mix short punchy sentences with longer, more complex ones. This creates rhythm and keeps readers engaged.
Tactic #11: Mobile Optimization & Responsive Design
Google uses mobile-first indexing, which means it primarily uses the mobile version of your content for ranking. If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, you’re in serious trouble.
Why Mobile-First Indexing Matters
More than 60% of searches now happen on mobile devices, and that percentage keeps growing. Google’s mobile-first approach means they crawl and index your mobile site before your desktop version.
If your mobile site is missing content, broken, or provides a poor experience, that’s what Google sees and judges. Your desktop version becomes secondary.
Testing & Improving Mobile User Experience
Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test tool to identify issues. Check your site on actual mobile devices—different screen sizes reveal different problems.
Ensure tap targets (buttons and links) are large enough and well-spaced. Nothing frustrates mobile users more than accidentally tapping the wrong link because everything’s too close together.
Make sure text is readable without zooming. Use font sizes of at least 16px for body text. And eliminate horizontal scrolling—everything should fit within the viewport width.
Bonus: On-Page SEO Checklist for Quick Wins
Let me give you two practical checklists you can use right away to improve your on-page SEO for Google ranking.
Pre-Publishing Checklist
Before you hit publish on any content, run through these checks:
- Primary keyword appears in title tag, H1, first paragraph, and URL
- Title tag is 50-60 characters and compelling
- Meta description is 150-155 characters with keyword and CTA
- At least one H2 includes a keyword variation
- Images are compressed and have descriptive alt text
- Internal links point to 2-3 relevant pages
- External links (if any) open in new tabs
- Content includes bullet points or lists for scannability
- Paragraphs are short (2-4 sentences)
- URL is clean, short, and includes keyword
Post-Publishing Optimization Tasks
After publishing, don’t just forget about your content:
- Submit URL to Google Search Console for indexing
- Check mobile-friendliness on actual devices
- Monitor Core Web Vitals in Search Console
- Add schema markup if you haven’t already
- Update internal links from older relevant content
- Share on social media to drive initial traffic
- Monitor rankings and adjust if needed after 2-4 weeks
Common On-Page SEO Mistakes That Kill Rankings
Even experienced marketers make these mistakes, and they can seriously damage your rankings.
Keyword Stuffing
Repeating your keyword unnaturally throughout your content looks spammy and actually hurts rankings now. Google’s algorithms easily detect this manipulation.
Focus on natural language and semantic variations. If you’re writing about on-page SEO services, use related terms like “on-page optimization,” “on-page techniques,” and “on-site SEO” throughout your content instead of repeating the exact phrase constantly.
Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content confuses Google about which version to rank and can dilute your ranking potential. This includes duplicate title tags, meta descriptions, or entire pages with the same or very similar content.
Every page needs unique, valuable content. If you have similar products or services, highlight what makes each one distinct.
Ignoring Page Speed
Slow pages lose visitors and rankings. If your page takes more than 3 seconds to load, you’re losing users and search visibility.
Compress images, minimize code, use caching, and consider a faster hosting provider. Page speed isn’t optional anymore—it’s a confirmed ranking factor.
Measuring Your On-Page SEO Success
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Track these metrics to know if your on-page SEO strategy is working.
Key Metrics to Track
Monitor your organic traffic growth over time. Use Google Analytics to see which pages attract the most visitors and which need improvement.
Track keyword rankings for your target terms. Are you moving up or down? Tools like SEMrush show ranking changes over time.
Watch your click-through rate in Google Search Console. High impressions but low clicks means your titles and descriptions need work.
Check your bounce rate and average time on page. High bounce rates suggest your content isn’t matching search intent.
Best Tools for On-Page SEO Analysis
Google Search Console
Slow pages lose visitors and rankings. If your page takes more than 3 seconds to load, you’re losing users and search visibility.
Compress images, minimize code, use caching, and consider a faster hosting provider. Page speed isn’t optional anymore—it’s a confirmed ranking factor.
SEMrush & Ahrefs
These paid tools provide comprehensive SEO analysis. They show keyword rankings, backlink profiles, competitive analysis, and on-page SEO audit features that identify technical issues.
Both offer on-page SEO checklist features that scan your content and suggest specific improvements.
PageSpeed Insights
Google’s free tool analyzes your page speed and Core Web Vitals. It provides specific recommendations for improvement with impact estimates.
Run this regularly, especially after making site changes, to ensure you haven’t accidentally slowed things down.
Conclusion: Your On-Page SEO Action Plan
We’ve covered a lot of ground here, and I know it might feel overwhelming. But here’s the truth: on-page SEO doesn’t have to be complicated or time-consuming once you understand the fundamentals.
Quick Implementation Steps
Start with your highest-traffic pages. Optimize those first because improvements will have the biggest immediate impact. Work through the tactics systematically—title tags, meta descriptions, headers, content quality, internal links.
Don’t try to perfect everything at once. Pick 2-3 tactics from this guide and implement them thoroughly this week. Then move to the next few tactics next week.
Next Steps for Long-Term Success
Make on-page SEO part of your content creation process, not an afterthought. Build these on-page SEO best practices into your workflow so every new page starts optimized.
Regularly audit your existing content. On-page SEO isn’t set-it-and-forget-it. Google’s algorithms evolve, and so should your pages. Review and update your top pages every 3-6 months.
And remember, Digi Segment and HV Digital Marketing are here to help if you need expert guidance implementing these strategies for your specific business.
FAQs
On-page SEO refers to optimizations you make directly on your website—content, HTML tags, site structure, and user experience. You have complete control over these elements. Off-page SEO includes factors outside your website, primarily backlinks from other sites, social signals, and brand mentions. While you can influence off-page factors, you can't directly control them like you can with on-page elements.
Typically, you'll start seeing ranking improvements within 2-4 weeks for low-competition keywords and less competitive pages. For more competitive terms, expect 3-6 months of consistent effort before significant movement. Remember that on-page SEO is cumulative—the more pages you optimize and the more authority your site builds, the faster you'll see results on new content.
Yes and no. Every page should meet basic on-page SEO standards—unique title tags, proper headers, optimized images, and good user experience. But you should prioritize deep optimization for pages that target important keywords or drive business results. Your homepage, service pages, and key blog posts deserve the most attention. Utility pages like privacy policies need less intensive optimization.
Forget about keyword density percentages—that's outdated advice from 2010. Modern on-page SEO focuses on natural language and topic coverage rather than hitting a specific keyword percentage. Include your primary keyword in key locations (title, H1, first paragraph, URL) and use related terms throughout. If your content reads naturally and comprehensively covers the topic, you're probably hitting the right keyword usage without counting.
For low-competition keywords, absolutely. On-page SEO can be enough to dominate search results. But for competitive terms, you'll need the full SEO package—strong on-page optimization plus quality backlinks, good site authority, and other off-page signals. Think of on-page SEO as the foundation. You can't build a strong house without a solid foundation, but the foundation alone isn't the entire house. Combine excellent on-page SEO with strategic link building and technical SEO for the best results.
I’m Hardik Vaghani, founder of HV Digital Marketing, a results-driven digital marketing agency. I specialise in SEO, Google Ads, and social media marketing, helping businesses grow their online presence with proven strategies. I’m passionate about creating high-quality, SEO-optimised blogs that educate readers and rank on Google. My goal is to turn ideas into measurable digital success through smart, ethical marketing.